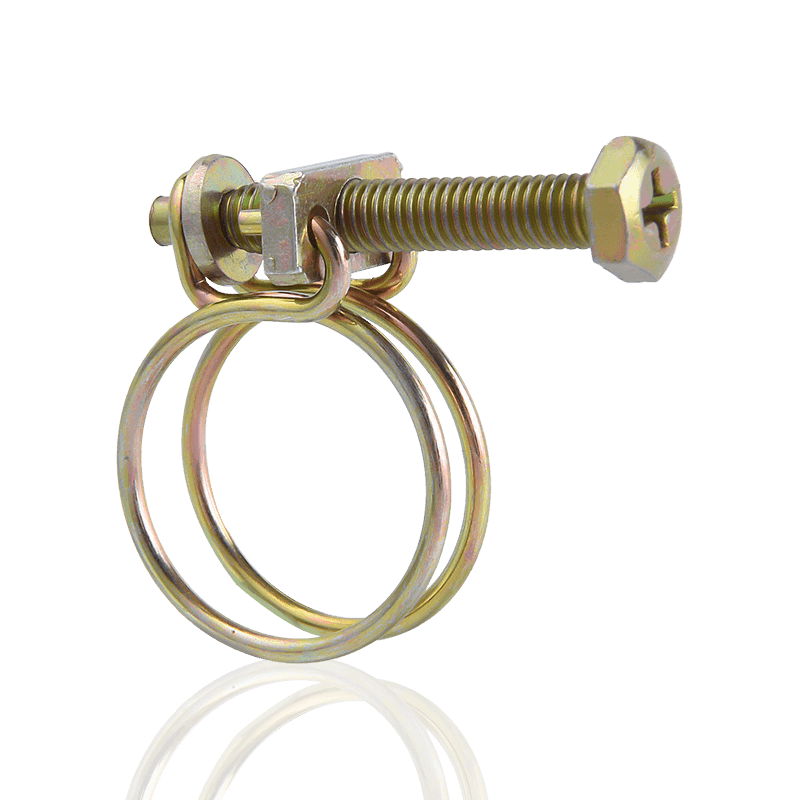
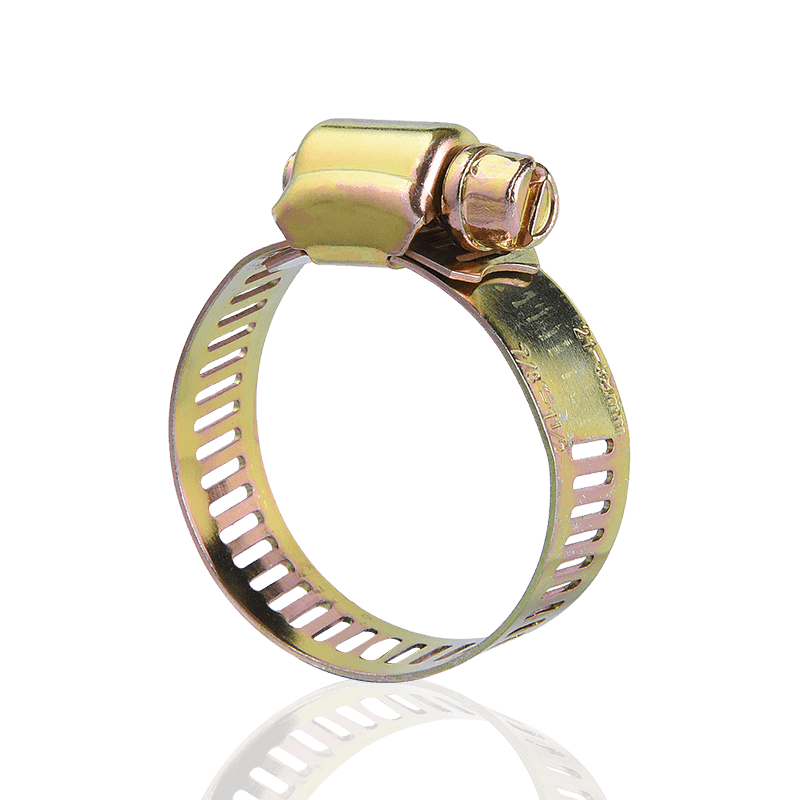What is the difference between German and American hose clamps?
 2025.09.19
2025.09.19
 Industry News
Industry News
American and German hose clamps differ significantly in design, manufacturing process, and application. Understanding these differences is important for selecting the best fastener for a specific application.
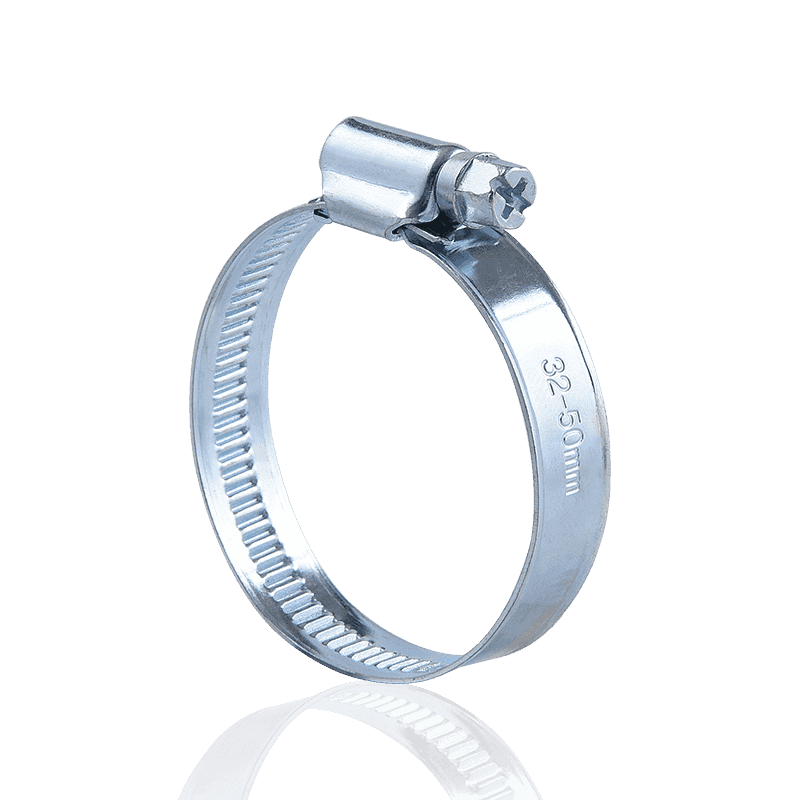
American Hose Clamps
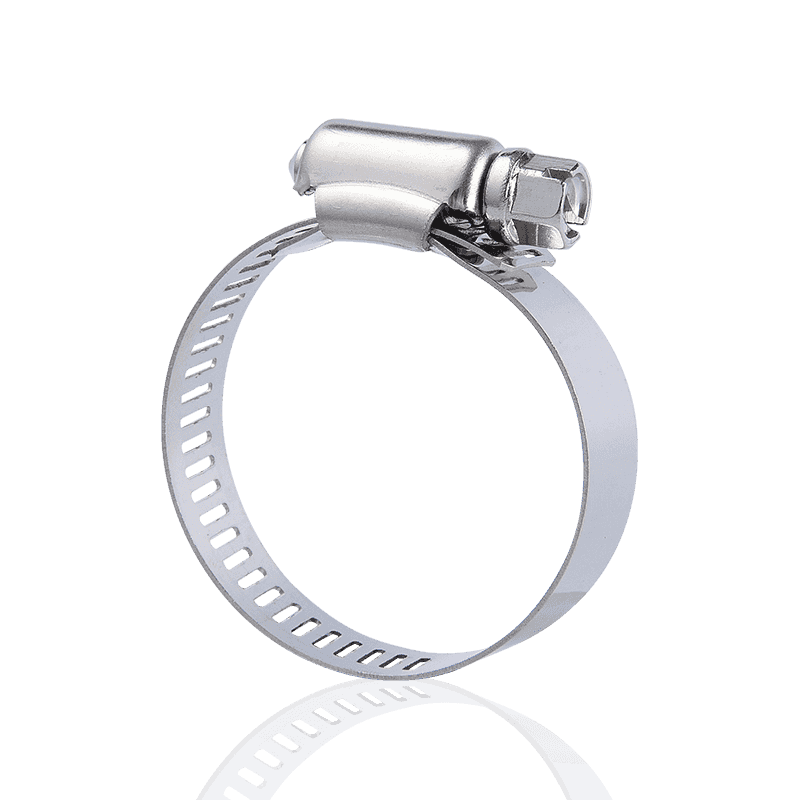
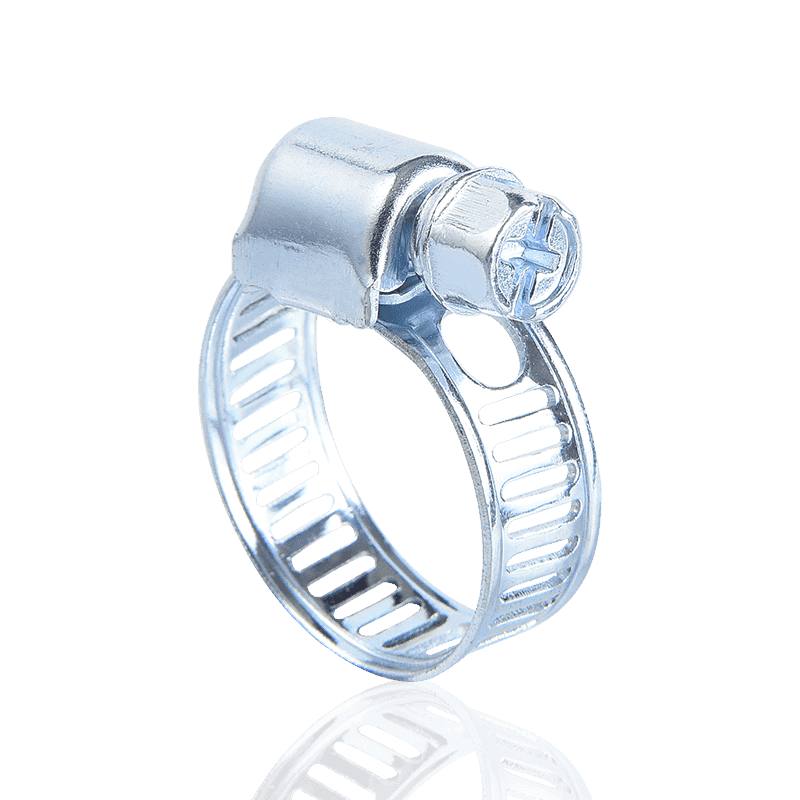
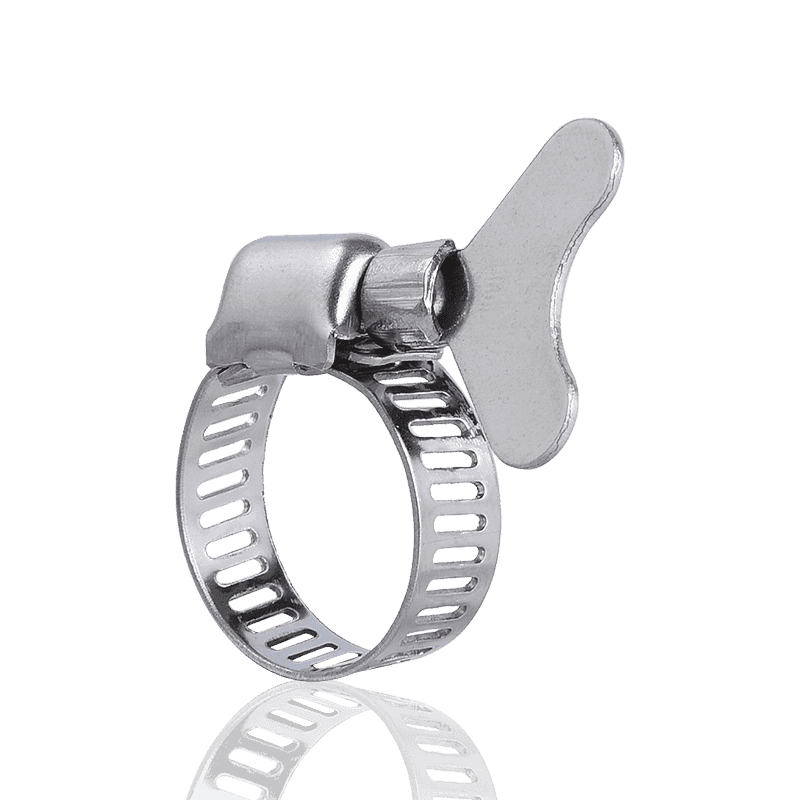
American hose clamps are typically manufactured using a through-hole process. This design allows the engagement grooves in the steel band to be continuous, with the screw teeth engaging directly within them. This structure provides greater torque and precise engagement during tightening, making them excellent in a wide range of fastening applications.
Key Features:
- Manufacturing Process: Through-hole stamping.
- Advantages: High torque, secure locking, and a wide adjustment range. The through-hole design allows the screw teeth to more effectively engage the steel band, providing strong clamping force.
- Applications: Widely used in industries such as automotive piping, water pumps, fans, and food and chemical machinery, they are particularly suitable for connecting flexible and rigid pipes.
- Material and Type: Common materials include stainless steel and carbon steel. There are various types, including small American, medium American, and large American styles, some with snap caps or handles.
However, it's important to note that because the steel band is hollow at the through-hole, while it offers greater tensile strength than German-style hose clamps, it may break at the hole under strong pulling.
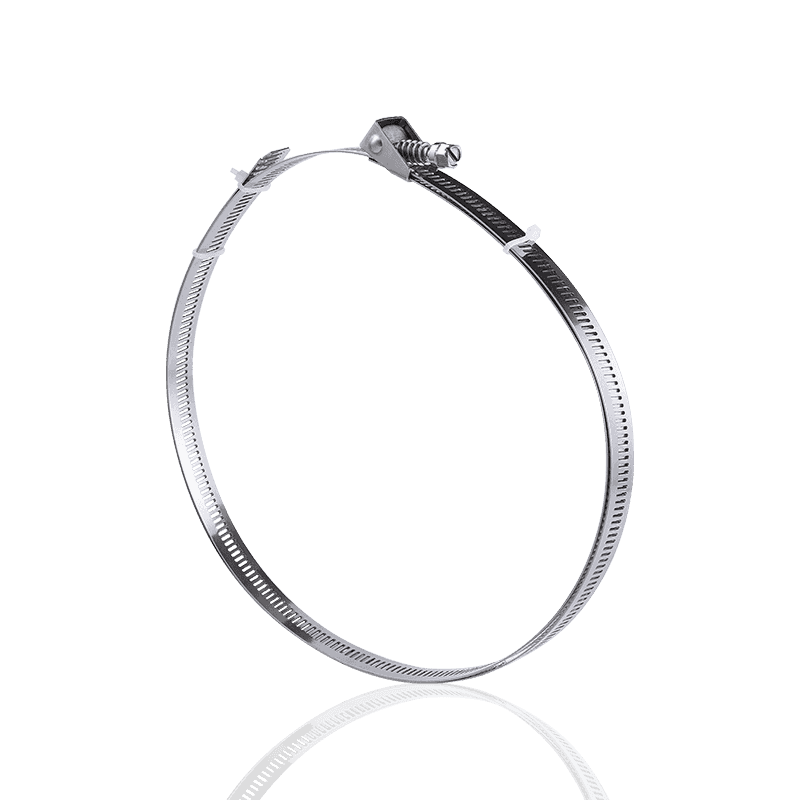
German-style hose clamps
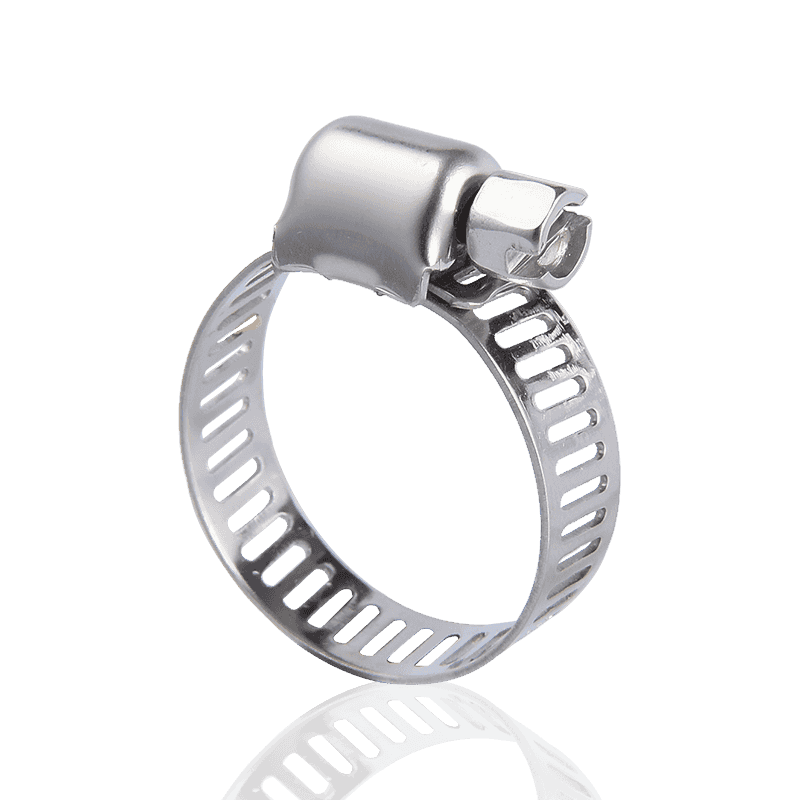
In contrast, German-style hose clamps are typically stamped rather than through-hole, resulting in a smooth, hole-free steel band surface. The threads are stamped or embossed into the steel band, with the screw teeth engaging these raised threads to create a secure lock.
Key Features:
- Manufacturing Process: Typically uses a hole-free stamping or embossing process.
- Advantages: The steel band is free of holes, resulting in higher structural strength and corrosion resistance. The threads engage evenly, providing stable clamping force.
- Applications: Commonly used in applications requiring high airtightness and pressure resistance, such as automotive exhaust systems, high-pressure piping, and equipment requiring aesthetically pleasing appearance.
- Material: Mostly stainless steel or galvanized carbon steel for excellent corrosion resistance.
The key difference between American-style and German-style hose clamps lies in their manufacturing process and the resulting performance characteristics.
| Features | American-style hose clamp | German-style hose clamp |
| Steel belt | Through-hole design | No holes, stamped threads |
| Locking method | Screw teeth embedded in the through-hole | Screw teeth interlock with the stamped threads |
| Torque | High torque and strong locking force | Uniform and stable locking force |
| Tensile strength | Strong, but may break at the through-hole | Strong steel band structure for enhanced pull resistance |
| Applicable scenarios | Universal hose connection, torsion-resistant and pressure-resistant | High-pressure, high-tightness requirements, especially for automotive exhaust systems |
American-style hose clamps are popular for their high torque and locking force, making them particularly suitable for applications requiring a secure connection. German-style hose clamps, on the other hand, offer high strength and excellent durability, making them a better choice for industrial applications requiring greater durability and airtightness. Choosing the right hose clamp depends on specific application requirements and performance priorities.
American-style hose clamps, on the other hand, offer high strength and excellent durability, making them a better choice for industrial applications requiring greater durability and airtightness. Choosing the right hose clamp depends on specific application requirements and performance priorities.