How does the German Hose Clamp ensure a stable connection of pipes, hoses or cables?
 2025.05.23
2025.05.23
 Industry News
Industry News
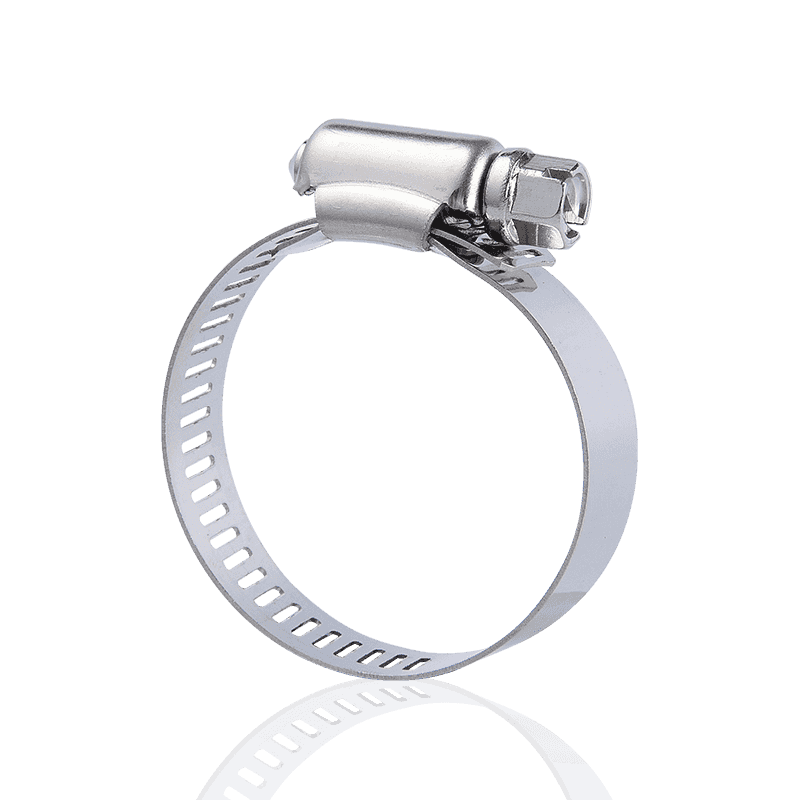
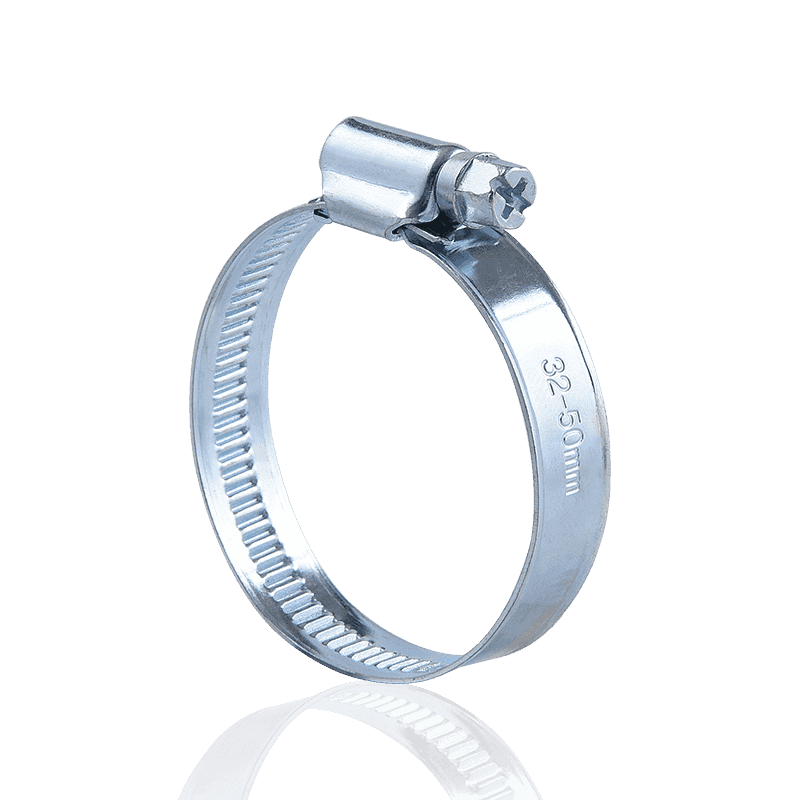
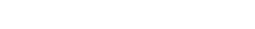
The main body of the German Hose Clamp steel belt is made of high-quality spring steel or stainless steel, which has both high strength and corrosion resistance. The surface is usually treated with rust prevention such as galvanizing to ensure that it will not deform after long-term use in a humid or corrosive environment. The width of the hoop is designed to be 9-12 mm. The wide structure can disperse the pressure, avoid local extrusion damage to the hose or cable, and enhance the sealing. The trapezoidal thread screw at the tail of the hoop is its core component. The thread bevel design can effectively convert the rotational force into a uniform linear clamping force, which is less likely to slip than ordinary threads. In addition, the hoop head and the steel belt are formed in one piece or precision welded to ensure that there is no risk of looseness at the connection, and the stability of the clamping force is guaranteed from the source.
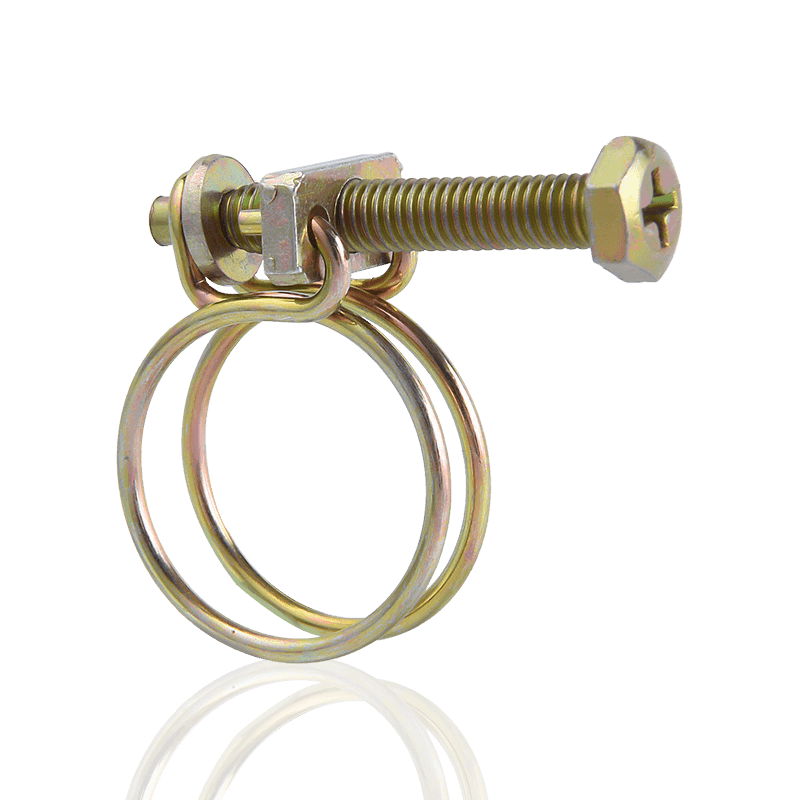
The German Hose Clamp achieves a stable connection through the synergy of mechanical transmission and pressure distribution. When the screw is rotated, the bevel of the trapezoidal thread converts the torque into the axial displacement of the hoop, so that the steel belt is gradually tightened. The thread design features an optimized bevel angle, which can provide sufficient friction to prevent reverse loosening and avoid deformation of the steel belt due to over-tightening. After the hoop is tightened, a 360° closed loop is formed, and the pressure is evenly distributed on the outer wall of the pipe, avoiding the risk of leakage caused by local stress concentration. At the same time, the self-locking structure designed at the end of the screw and the hoop can automatically lock after reaching the preset clamping force, and can maintain the connection stability even in the face of long-term vibration or pressure fluctuations.
First, the hoop needs to be initially inserted into the pipe and manually tightened until the pipe can be slightly rotated to avoid subsequent adjustment difficulties due to initial over-tightening. Then use a tool to rotate the screw for fine adjustment. It is recommended to tighten it step by step in stages, and check whether the pipe is displaced or deformed after rotating 1/4 turn at each stage. After installation, it is necessary to visually or manually confirm that the hoop has no warping edges and the screw is not loose. In daily maintenance, it is recommended to check the status of the throat clamp every 6-12 months, especially in high temperature, high humidity or vibration environments, and focus on observing the rust of the screw and the elastic attenuation of the hoop, and replace it in time if necessary.
For special-shaped pipe fittings, its wide band can fit the surface through elastic deformation, and cooperate with the fine-tuning function of the screw to achieve a tight connection; for pipes with rough surfaces, the high strength of the steel band and the bite force of the trapezoidal thread can overcome the friction resistance and ensure that the clamping force does not decay. In industrial scenarios, its high temperature resistance makes it suitable for high temperature environments such as engine cooling systems and steam pipes; in outdoor scenarios, the galvanized layer or stainless steel material can resist salt spray corrosion and ensure the long-term reliability of seaside equipment or agricultural irrigation systems.
In the field of automobile maintenance, it is often used to connect rubber fuel pipes and cooling water pipes in the engine compartment. Its oil resistance and vibration resistance can effectively prevent the joints from falling off or leaking; in the chemical industry, it is used to connect PVC hoses for conveying corrosive media. The combination of galvanized steel bands and trapezoidal threads can resist chemical media erosion; in home scenarios, it is used for water purifier pipelines, gas hoses, etc., and can be installed with simple tools, and the rounded corners of the band edges avoid scratching operators.