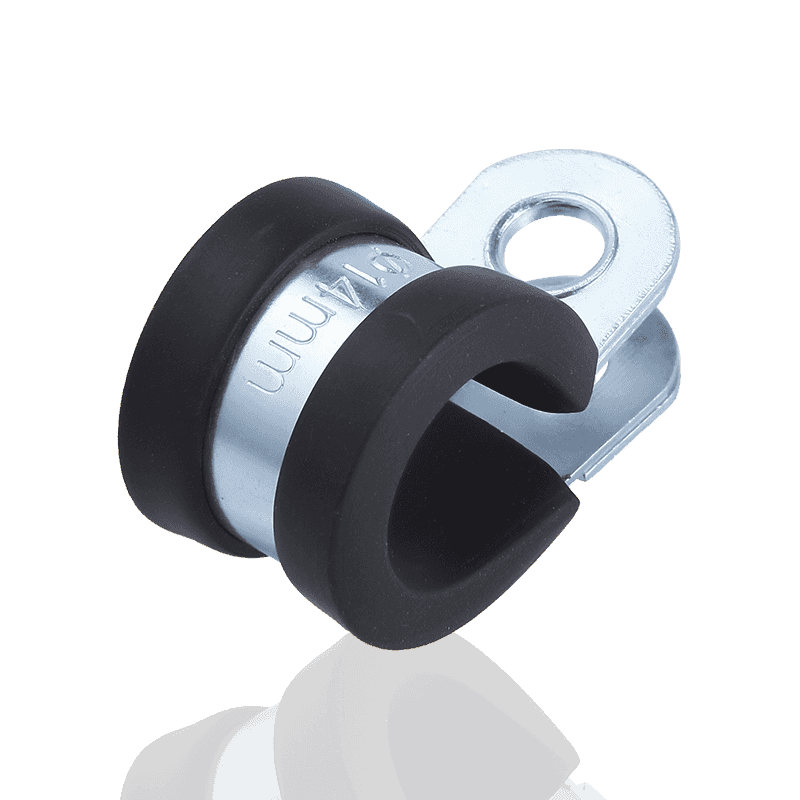Which hose clamp has the strongest clamping force?
 2025.12.05
2025.12.05
 Industry News
Industry News
In various fluid transport systems, hose clamps are key components ensuring the airtightness and liquid tightness of connections. Choosing a clamp with the strongest clamping force is crucial for ensuring system safety, preventing leaks, and improving equipment reliability.
Hose Clamp Basics: Why is Clamping Force Crucial?
The main function of a hose clamp is to provide uniform and sufficient radial pressure to tightly secure hoses (such as silicone hoses, rubber hoses, PVC hoses, etc.) to the joint. Under conditions of high pressure, high temperature, or severe vibration, insufficient clamping force will lead to:
- Liquid or gaseous media leakage
- Hose detachment from the joint
- Increased maintenance costs
- Enhanced safety risks
Therefore, one of the most critical indicators for evaluating hose clamp performance is the maximum and most durable clamping strength it can provide.
Mainstream Hose Clamp Types and Their Clamping Force Analysis
Hose clamps with different design principles have different focuses in terms of clamping force. Here are some common types of clamping clamps on the market and their clamping force characteristics:
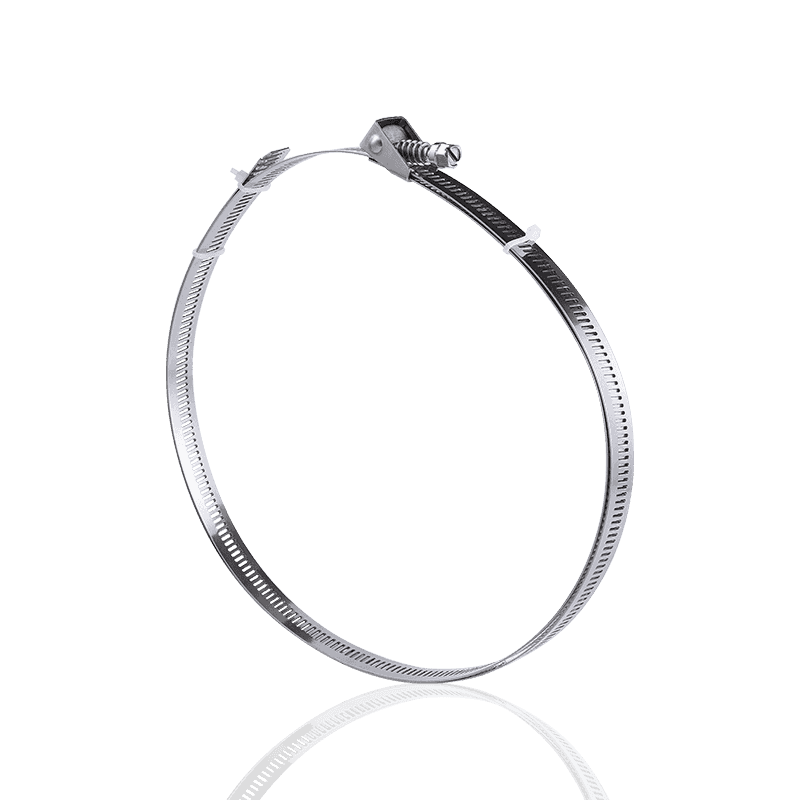
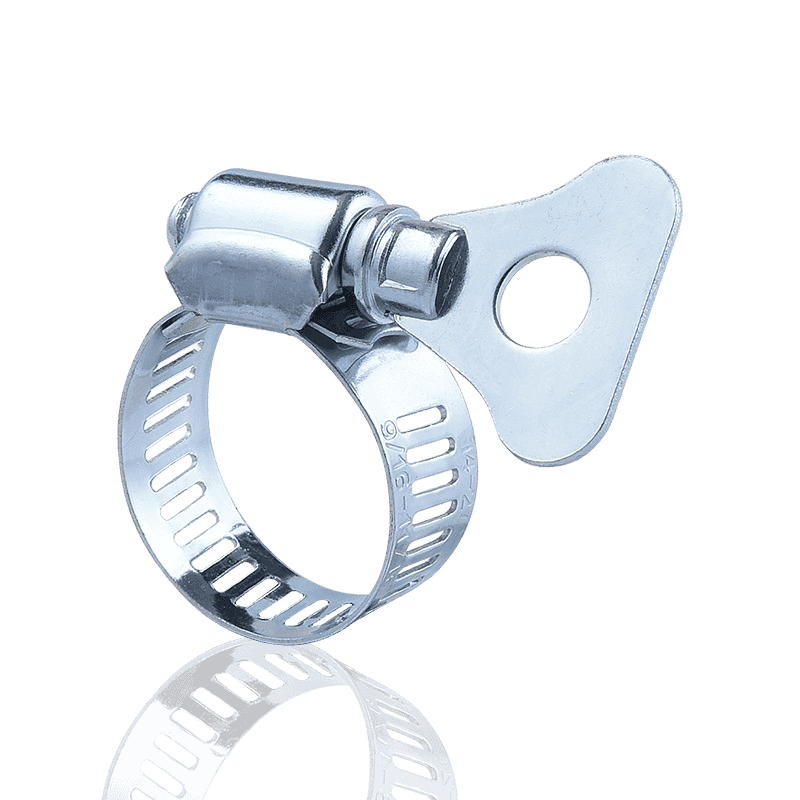
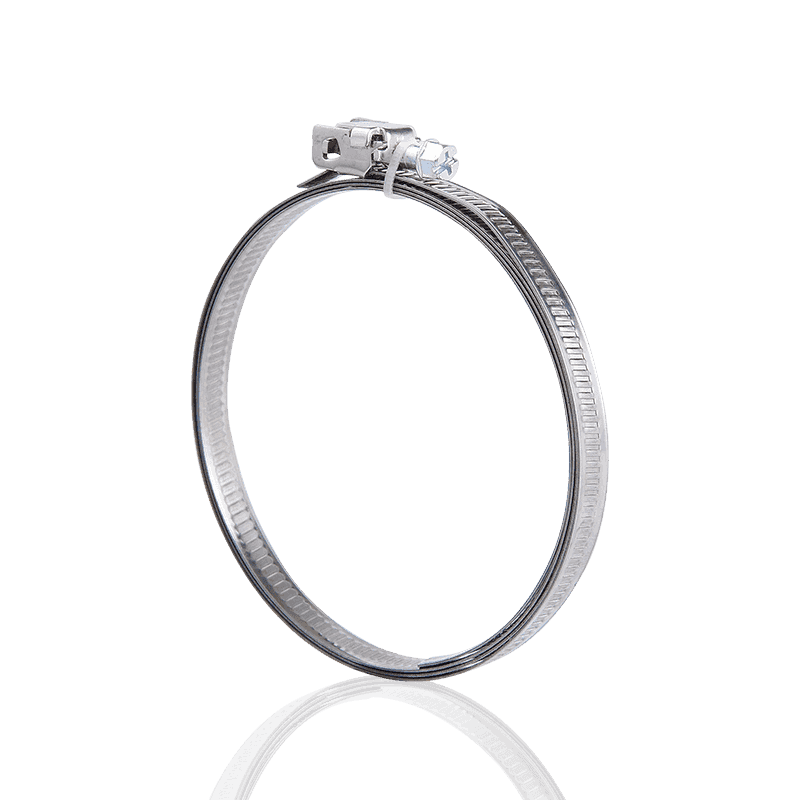
1. Worm Gear Clamps
Design Features: The most common type, tightening is achieved by a screw driving a perforated or stamped band.
Clamping Force Performance: Good. A large preload can be obtained by tightening the bolt. The strength and uniformity of its clamping force largely depend on the width and thickness of the clamp band, as well as the torque of the bolt.
Applications: Highly versatile, suitable for low to medium pressure automotive, industrial, and garden hose connections.
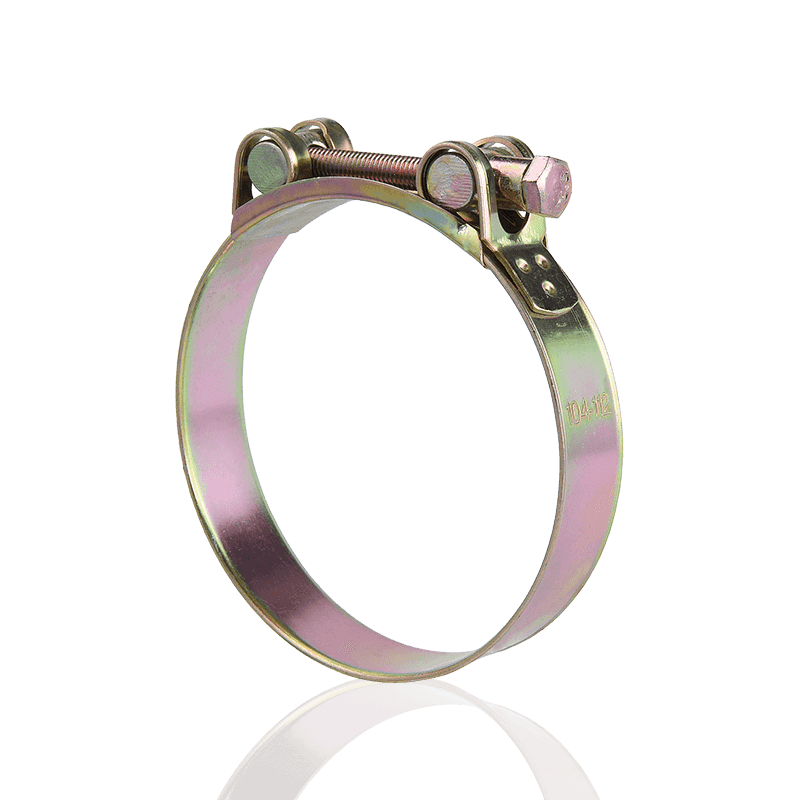
2. T-Bolt Clamps
Design Features: Uses a T-bolt and nut to tighten the clamp band.
Clamping Force Performance: Very strong. The T-bolt design allows it to withstand higher torque and clamping loads, providing more uniform and stronger radial pressure than traditional worm gear clamps. It is usually equipped with welded bridging or liners to prevent the band from squeezing the hose.
Application Scenarios: High-pressure, heavy-load, and high-vibration environments, such as turbochargers, heavy machinery, chemical plants, and marine exhaust systems.
3. V-Band Clamps
Design Features: Consists of two flanges and a V-ring, secured by a T-bolt or quick-release mechanism.
Clamping Force Performance: Strongest and most uniform. V-band clamps do not directly clamp the hose; instead, they tightly press two rigid flanges together. Their design advantage lies in providing 360° uniform sealing pressure and withstanding extremely high internal pressures.
Application Scenarios: Primarily used for turbocharger exhaust pipes, engine components, and other rigid pipe connections requiring quick disassembly and high-strength sealing.
4. Spring/Constant Torque Clamps
Design Features: Utilizes the elastic properties of spring steel to automatically adjust the clamping force in response to changes in ambient temperature (thermal expansion and contraction).
Clamping Force Performance: Moderate, but with excellent clamping stability. While the maximum clamping force may not be as high as a T-bolt, it ensures that the clamping force remains within a preset effective range even under drastic temperature changes, effectively preventing cold start leaks.
Application Scenarios: Automotive cooling systems, engine radiator hoses, and other fluid systems sensitive to temperature changes.
Conclusion: Which hose clamp has the strongest clamping force?
From the perspective of pure maximum clamping load:
T-bolt clamps and V-clamps offer the highest clamping strength. V-clamps excel in rigidity and uniformity, while T-bolt clamps are recognized as the "powerhouse" in high-pressure hose connections.
When selecting hose clamps for a specific application, always consider the following factors:
- Maximum operating pressure: The higher the pressure, the more necessary a T-bolt or V-clamp is.
- Temperature variations: If thermal expansion and contraction are present, consider constant force clamps to maintain a stable clamping force.
- Hose Material: For flexible or easily damaged hoses, choose clamps with linings or chamfered designs to prevent damage from excessive concentration of clamping force.
Choosing the right hose clamp means choosing system reliability. For applications requiring the strongest clamping force, prioritize T-bolts or V-bolt designs and ensure installation to the manufacturer's specified torque.