What are the differences between German and American type hose clamps?
 2025.12.26
2025.12.26
 Industry News
Industry News
In the field of fluid connection and fastening systems, American Hose Clamps and German type hose clamps are the two most common standards. While their basic function is to secure hoses and fittings, they differ significantly in structural design, force distribution, and the level of protection provided to the hose.
1. Structural Design: Perforated vs. Non-Perforated Strips
This is the most obvious difference:
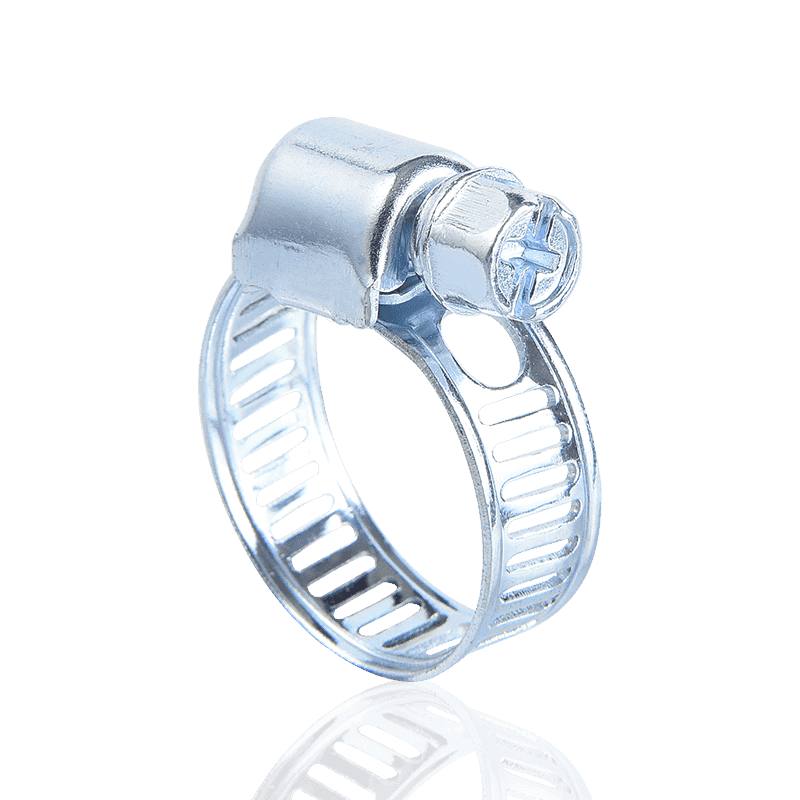
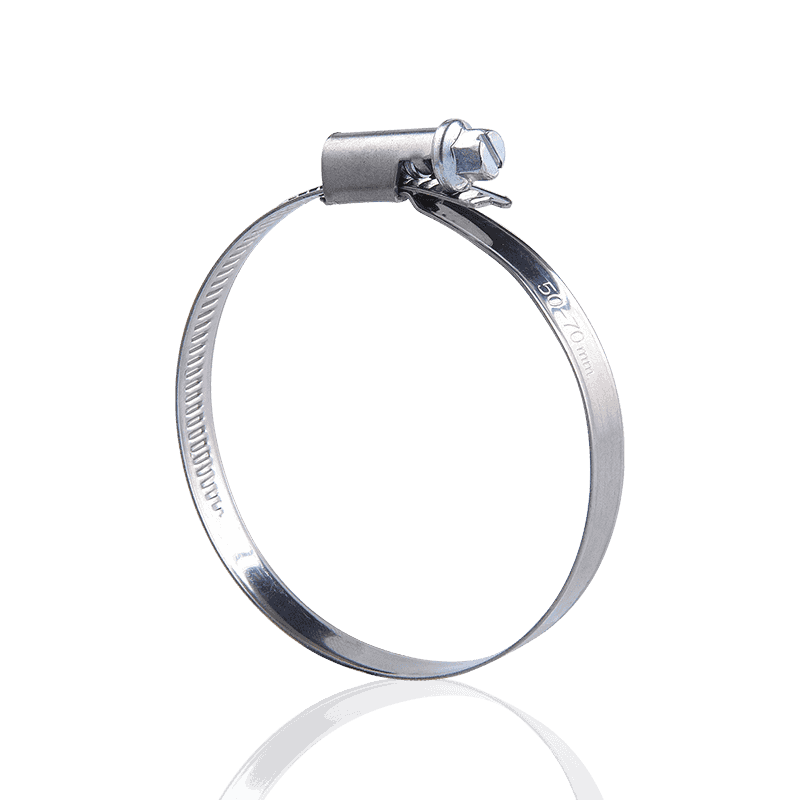
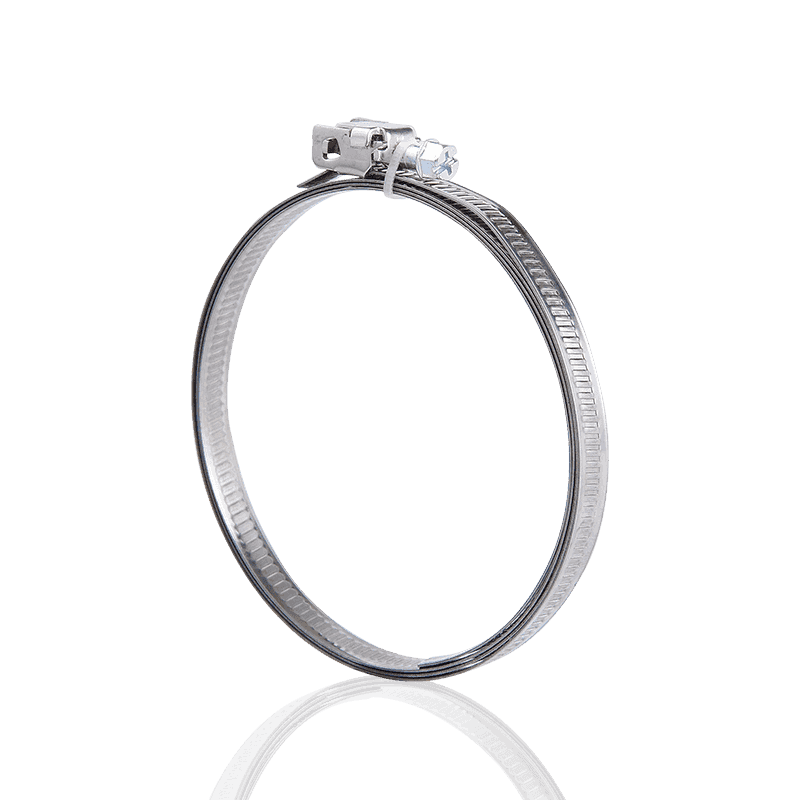
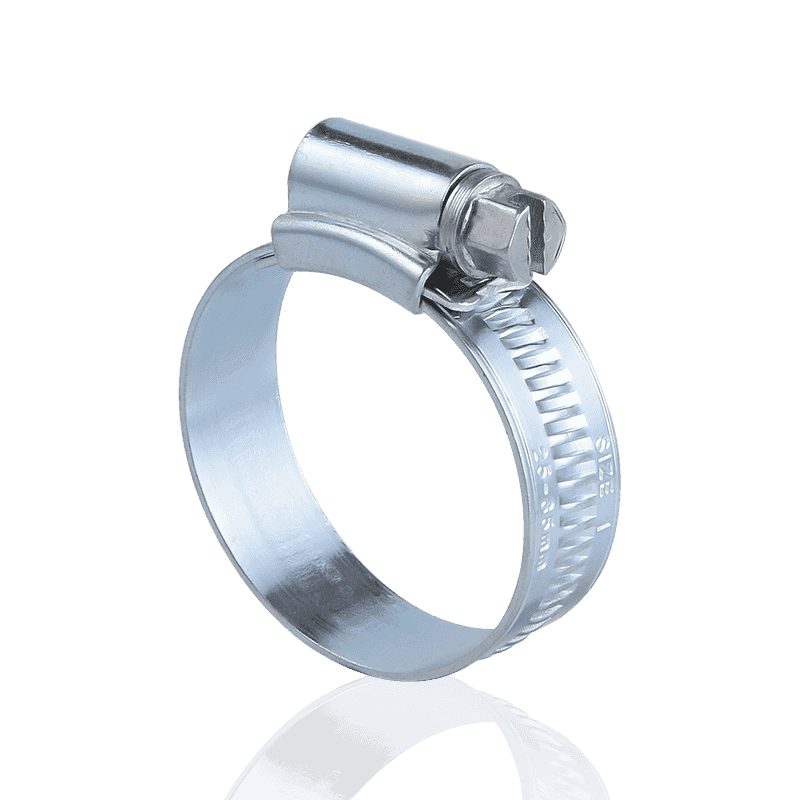
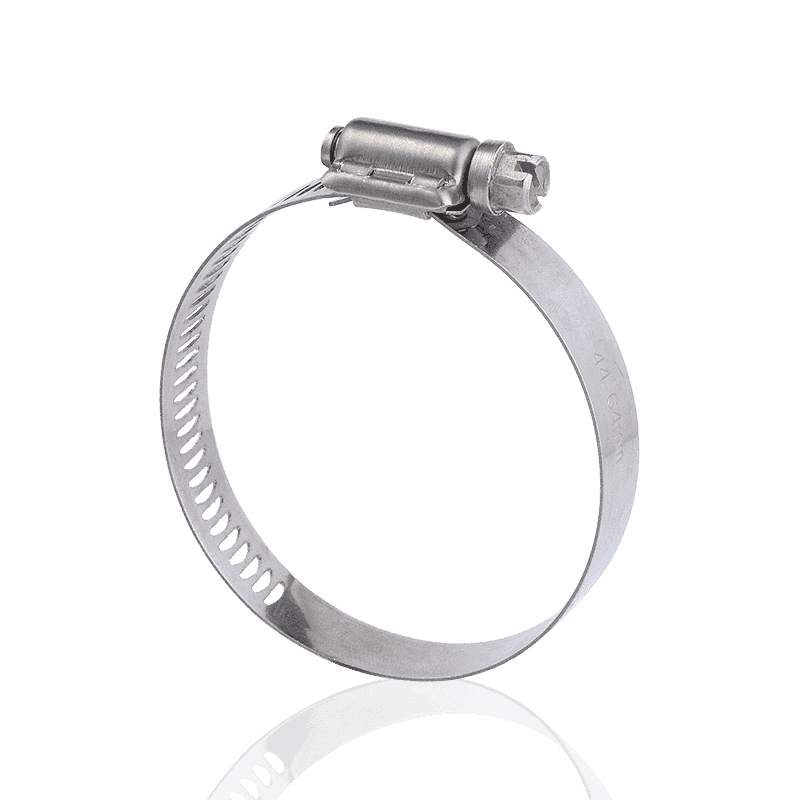
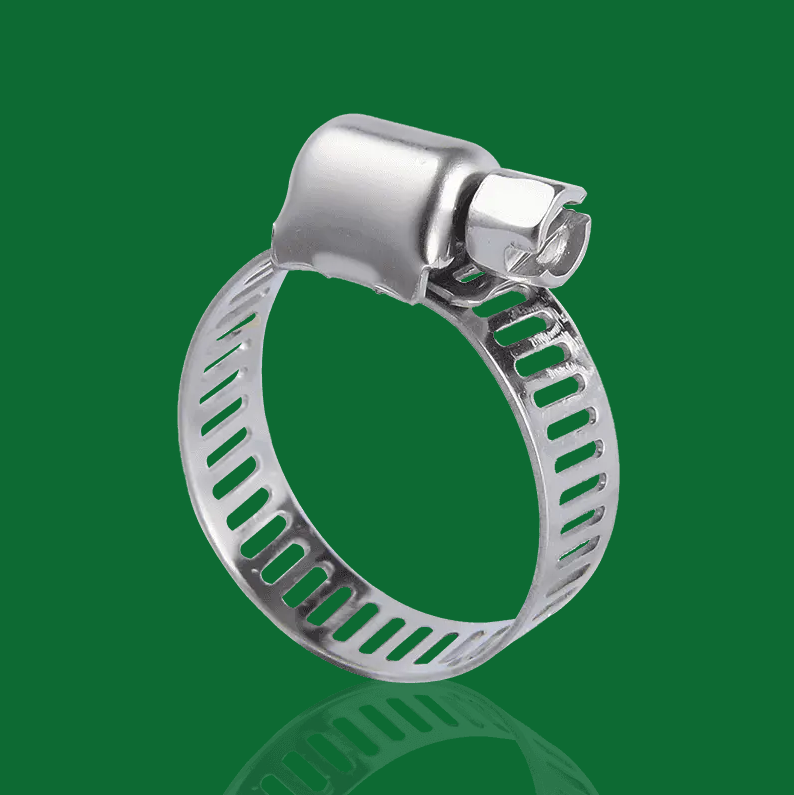
- American type hose clamps: Typically use a "perforated strip" design. Rectangular holes are directly punched into the steel strip, and the threads of the worm gear screw directly engage these holes to generate tension.
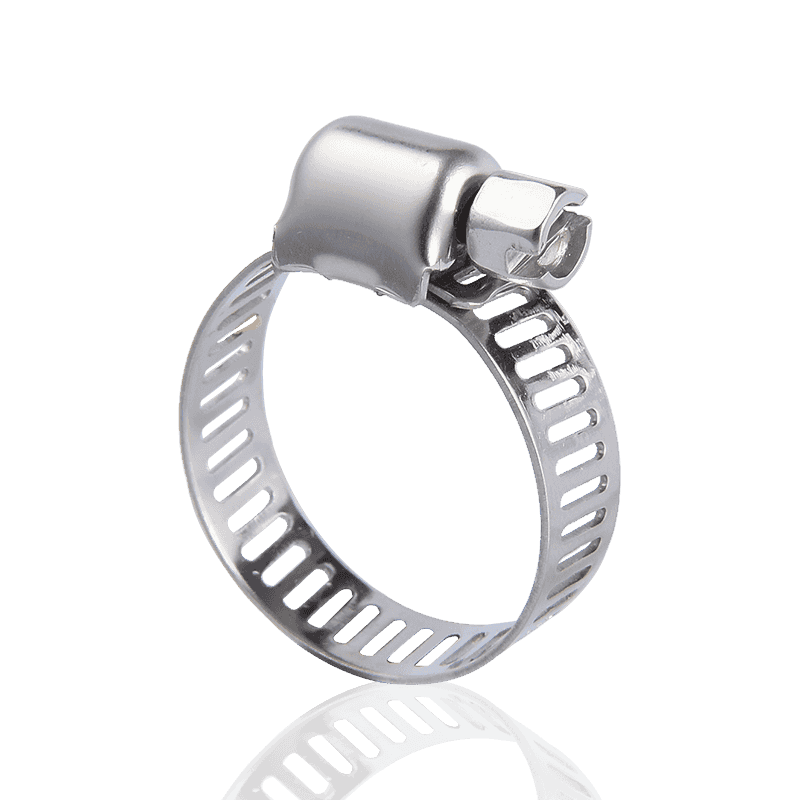
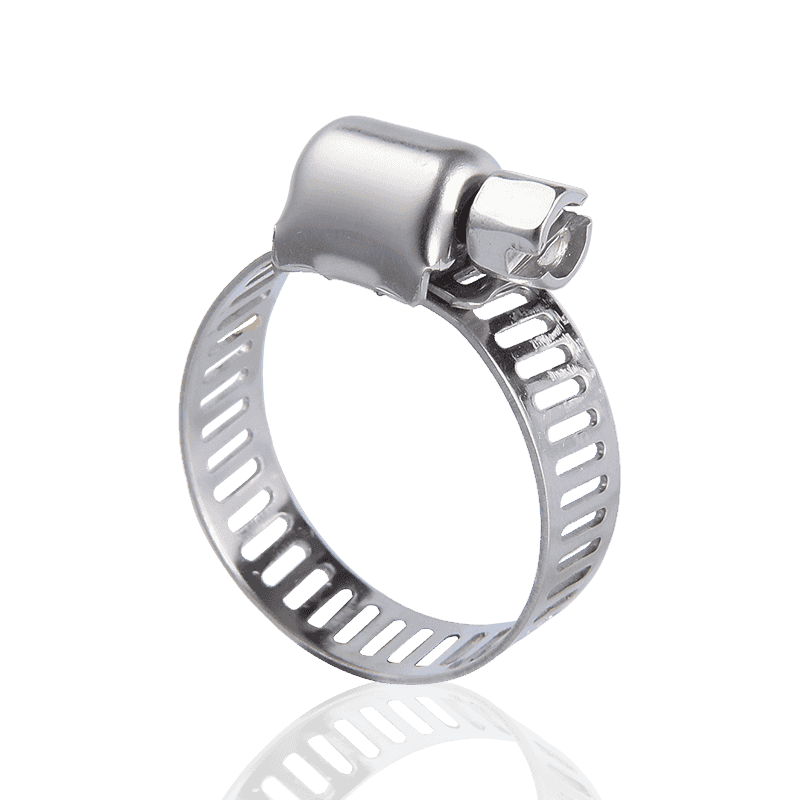
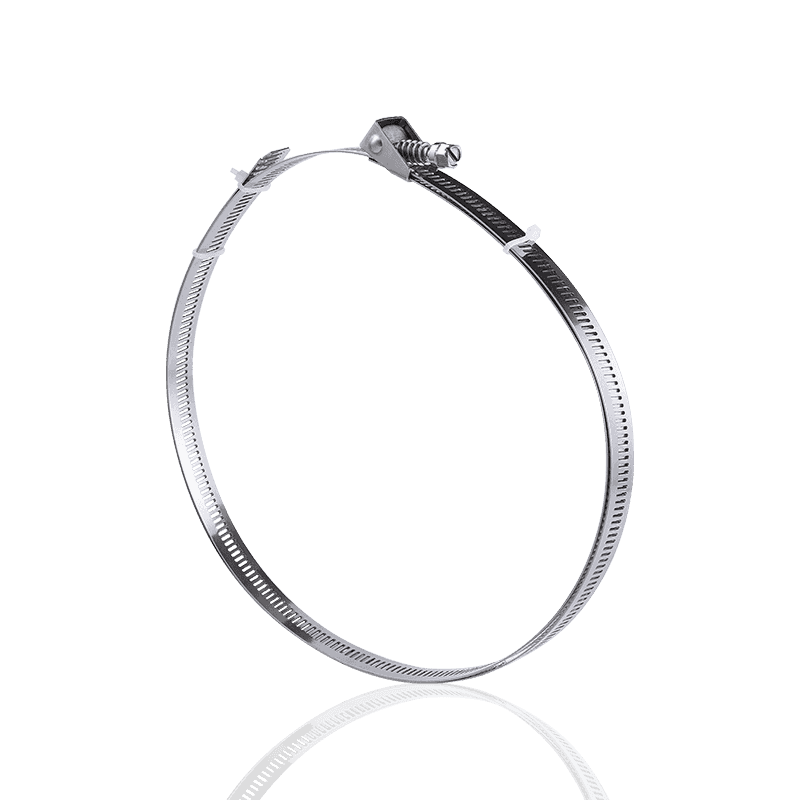
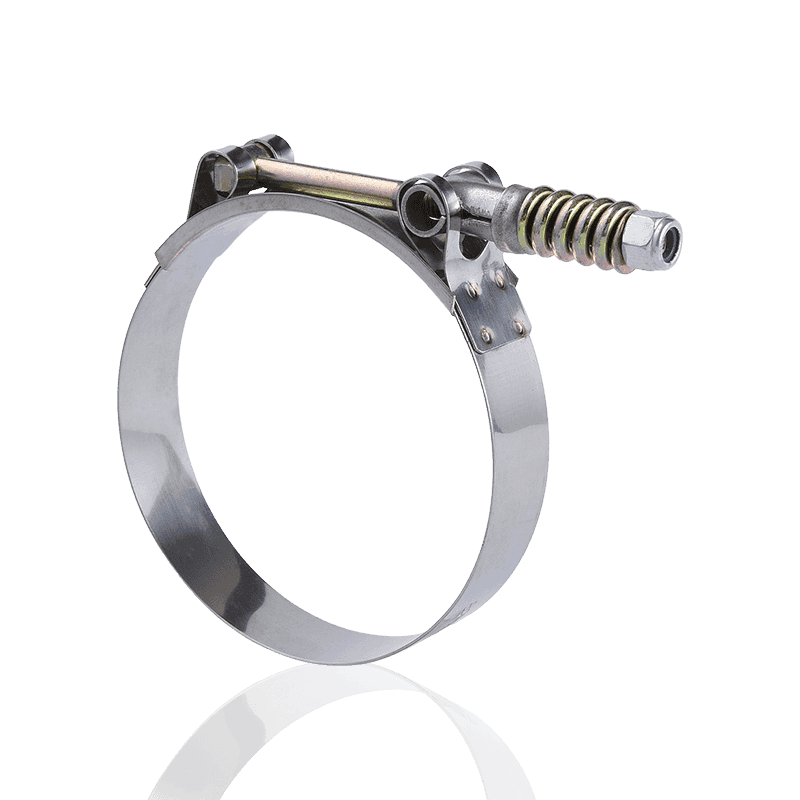
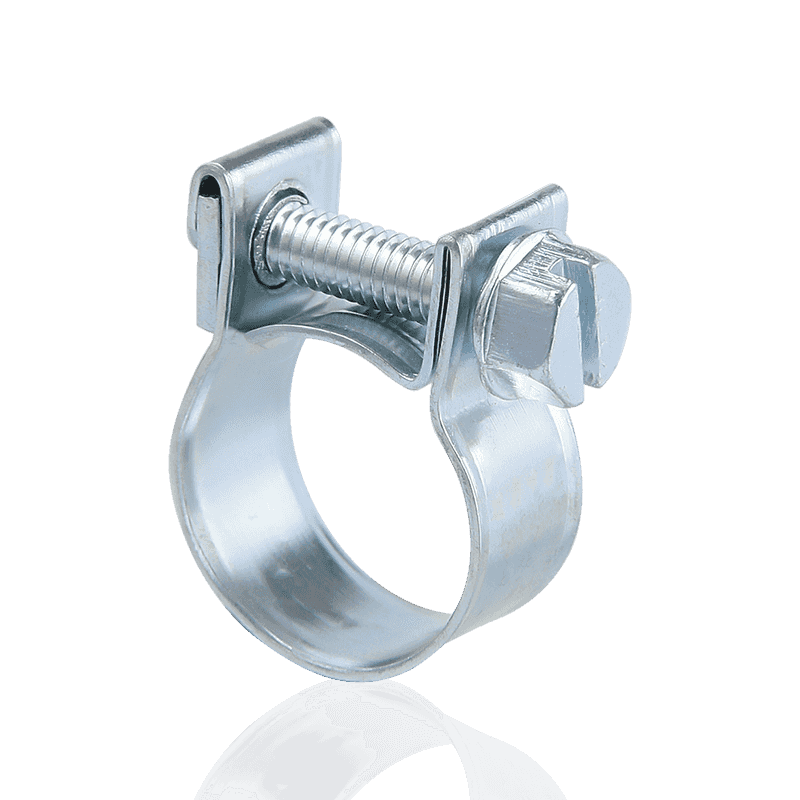
- German type hose clamps: Use a "non-perforated strip" design. The steel strip surface is smooth, and the grooves are formed by embossing; the threads engage at these embossed points.
2. Degree of Hose Protection
When selecting fasteners, the integrity of the hose is a key consideration:
- Characteristics of American hose clamps: Due to the through-holes in the steel strip, the rubber material of the hose can easily be "squeezed out" from the holes during high-pressure tightening. This not only damages the hose surface but may also cause cracks at areas of concentrated shear force, shortening the hose's lifespan.
- Advantages of German hose clamps: The smooth inner wall and flanged edge design ensure that the hose will not be cut or scratched during tightening, making them particularly suitable for silicone hoses or thinner hoses.
3. Width and Tightening Performance
Width Difference: Standard widths for American hose clamps are typically 8mm, 10mm, 12.7mm, etc. German clamps commonly have widths of 9mm and 12mm.
Stress Uniformity: The design of German clamps often provides more uniform radial pressure, while American clamps, due to their perforated structure, may experience steel strip tensile deformation under extreme high torque.
Key Differences Between German and American Hose Clamps
1. Differences in Steel Strip Structure Design
- American Hose Clamps: Employ a typical "perforated strip" structure. Rows of through rectangular holes are directly punched into the steel strip, serving as the stress points for the worm gear screw during rotation.
- German Hose Clamps: Utilize a "non-perforated/embossed" structure. The steel strip has a smooth interior and an external serrated surface formed by embossing. This design significantly enhances the tensile strength of the steel strip.
2. Hose Protection Performance
- American Hose Clamps: Due to the physical holes, the rubber material of the hose is easily squeezed out and cut during high-pressure tightening, causing mechanical damage to the hose surface.
- German Hose Clamps: The inner wall is smooth, and the edges typically have an outward-curving arc (flanged design). This ensures that the clamp will not cut or scratch the hose during strong tightening, providing better protection for precision or expensive hoses.

3. Common Material Selection
- American Hose Clamps: The most common materials on the market are 201, 304, or 316 series stainless steel, offering good corrosion resistance and suitability for various industrial environments.
- German Hose Clamps: In addition to common stainless steel, high-quality galvanized steel versions are also frequently offered, widely used in European machinery standards where material durability is a specific requirement.
4. Typical Application Area Comparison
- American Hose Clamps: Due to their high cost-effectiveness and ease of installation, they are widely used in automotive repair, civil piping, general agricultural irrigation, and ordinary industrial fluid connections.
- German Hose Clamps: With their excellent sealing uniformity and hose protection capabilities, they are mainly used in European automotive manufacturing, precision instrument systems, high-end machinery, and industrial pipelines sensitive to pressure fluctuations.
5. Installation and Operation Experience
- American Hose Clamps: The screw head design is flexible, typically supporting installation with flathead screwdrivers, Phillips screwdrivers, or hex sockets.
- German hose clamps: Their bolt heads have a compact design, and it's generally recommended to use a professional hex socket tool for operation to ensure more stable and precise torque transmission.
If your environment is cost-sensitive and the hose material itself is tough (such as ordinary reinforced rubber tubing), American hose clamps are a very practical choice due to their mature supply chain and high cost-effectiveness.
However, if your application involves high-precision equipment, expensive silicone hoses, or has extremely high sealing requirements (such as turbocharged systems), German hose clamps offer better safety.