What are the Three Types of Hose Clamps?
 2025.11.01
2025.11.01
 Industry News
Industry News
In industrial and everyday applications, hose clamps are essential components for connecting and securing hoses, pipes, or conduits. They ensure the sealing, reliability, and safety of connections, which is especially crucial in fluid transmission systems subjected to pressure or vibration. As an important fastener, understanding the main types of hose clamps helps in selecting the most suitable products for specific applications.
Hose clamps can be mainly divided into the following three types:
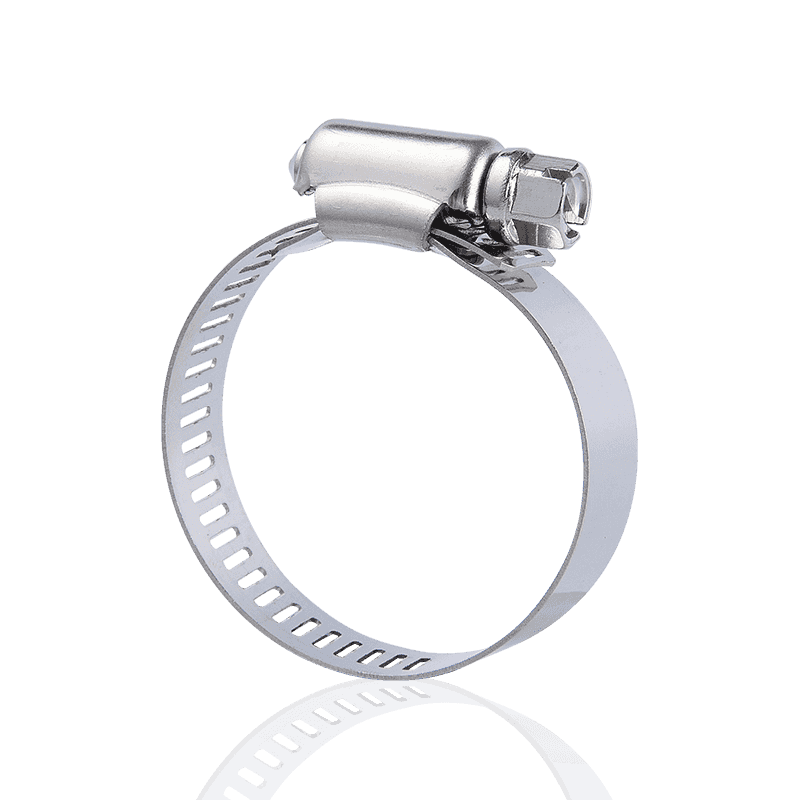
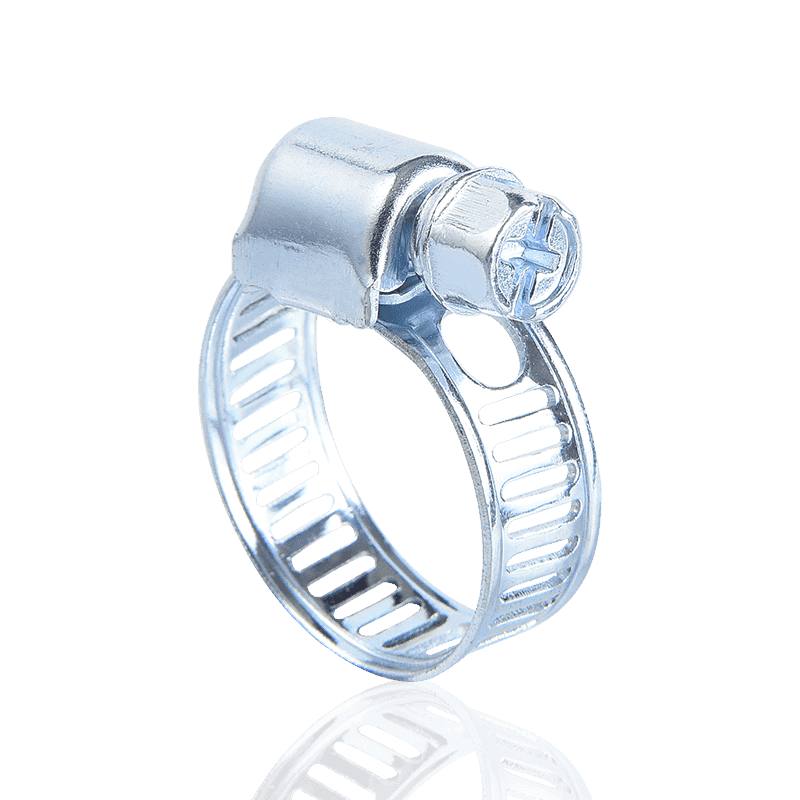
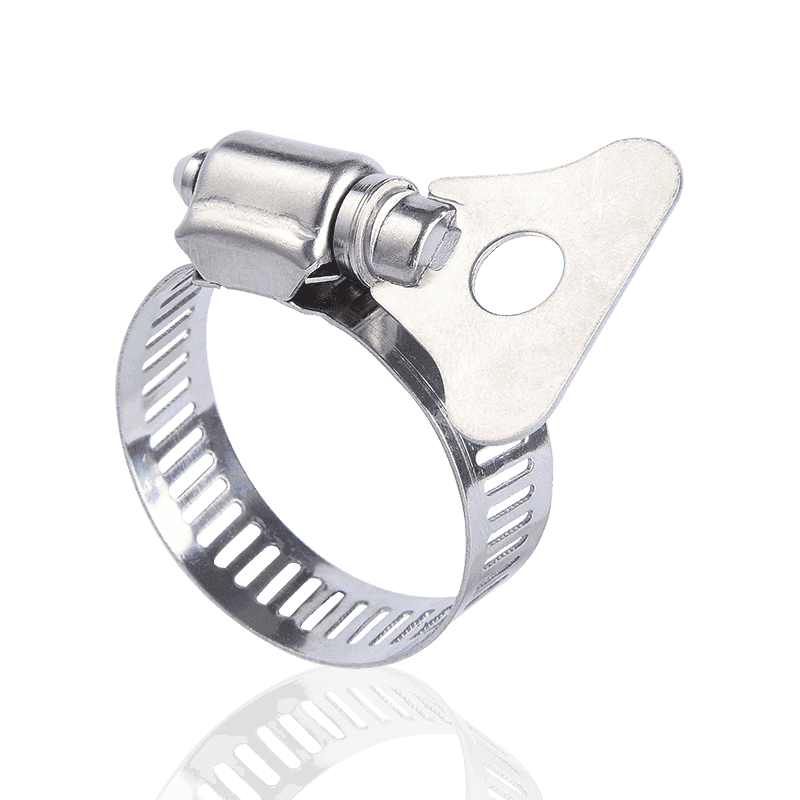
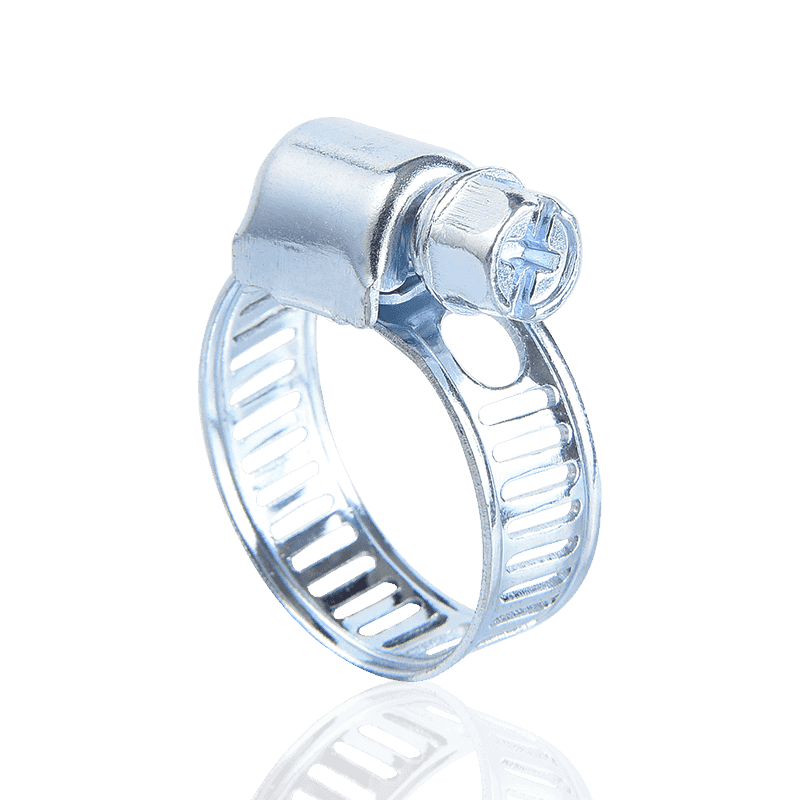
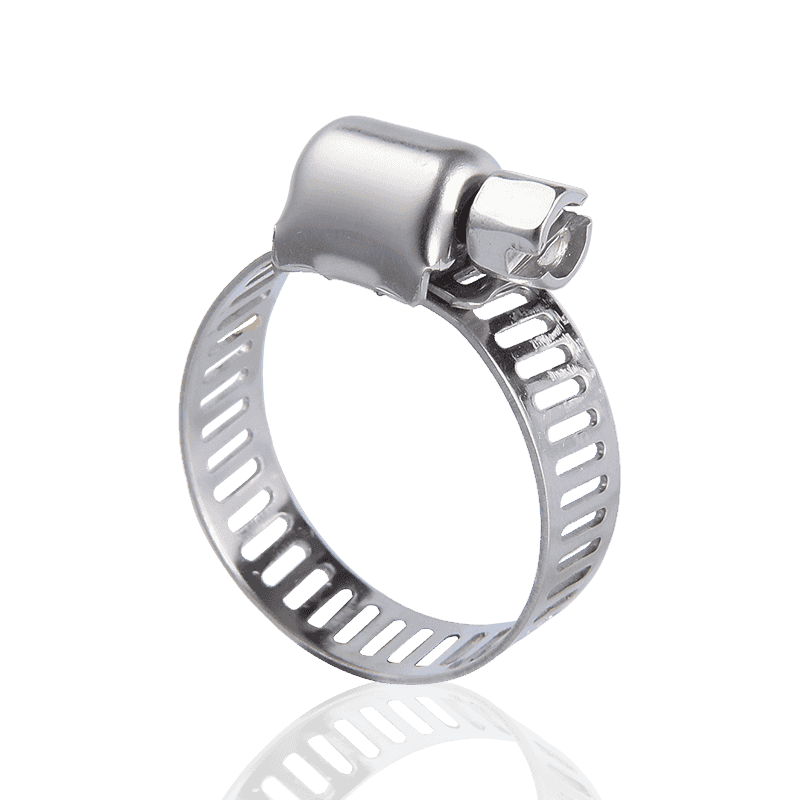
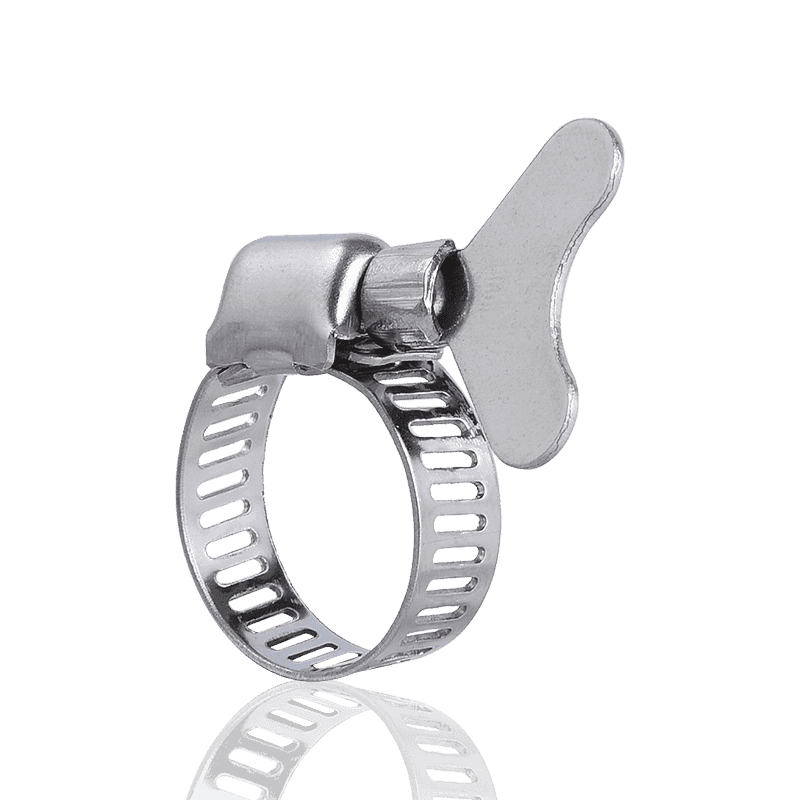
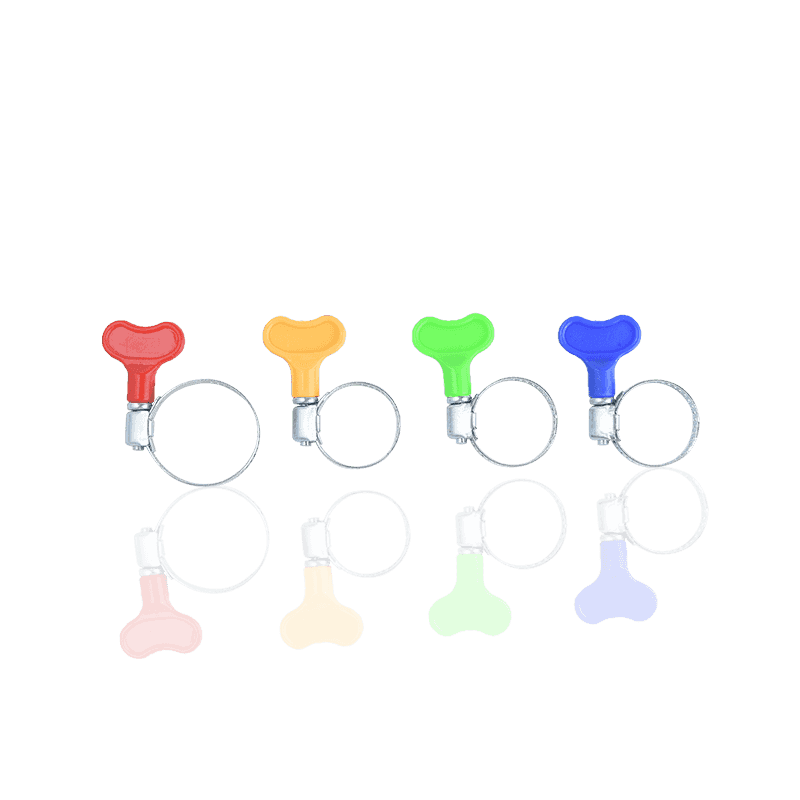
1. Thread-Driven Clamps
This is the most common and widely used type of hose clamp on the market, often referred to as "hose clamps" or "screw clamps."
Features and Principle: Thread-driven clamps consist of a screw and a steel strip (or clamping strip) with continuous slots. When the screw is turned, the threads on the screw engage with the slots on the steel strip, causing the steel strip to tighten, thus applying a uniform tightening force.
Subtypes: Common subtypes include American-style hose clamps and German-style hose clamps.
- American-style hose clamps (as described in your saved information) typically use a through-hole process, offering torsional and pressure resistance, balanced torsional torque, precise engagement, secure locking, and wide applicability.
- German-style hose clamps typically use a stamping process instead of a through-hole process, generally providing a more uniform 360-degree sealing pressure.
Applications: Due to their ease of installation, wide adjustability, and cost-effectiveness, threaded clamps are widely used in automotive (e.g., automotive piping), plumbing systems, home gardening, and general industrial connections. For more information, check out our hose clamp options.
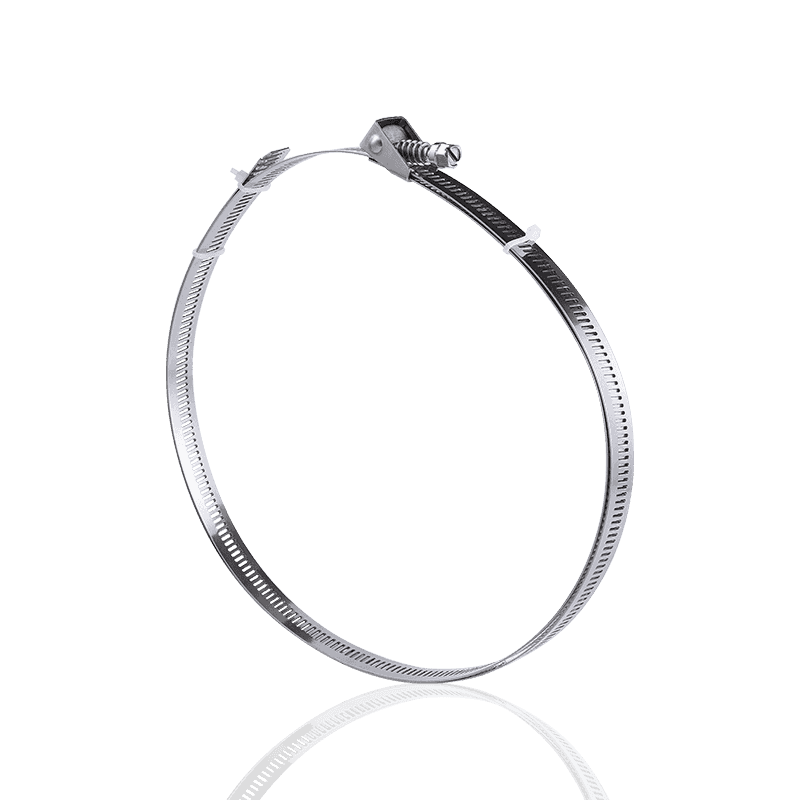
2. Spring Clamps
Spring clamps are self-tightening or constant-force clamps designed to maintain a constant clamping force as hoses expand or contract due to temperature changes.
Features and Principle: These clamps are typically made of spring steel and clamp the hose through their own elasticity. They have no screws or other mechanical adjustment mechanisms. The spring steel ring, designed to be pre-tensioned, continuously applies a constant pressure after installation.
Advantages: The biggest advantage is the "constant stress." When engine or system temperatures rise, hoses expand; when temperatures drop, hoses contract. Spring clamps automatically compensate for these dimensional changes, effectively preventing leaks caused by thermal expansion and contraction.
Applications: Widely used in environments with significant temperature fluctuations, such as automotive cooling systems and engine air or vacuum lines. For more details, you can explore our hose clamp collection.
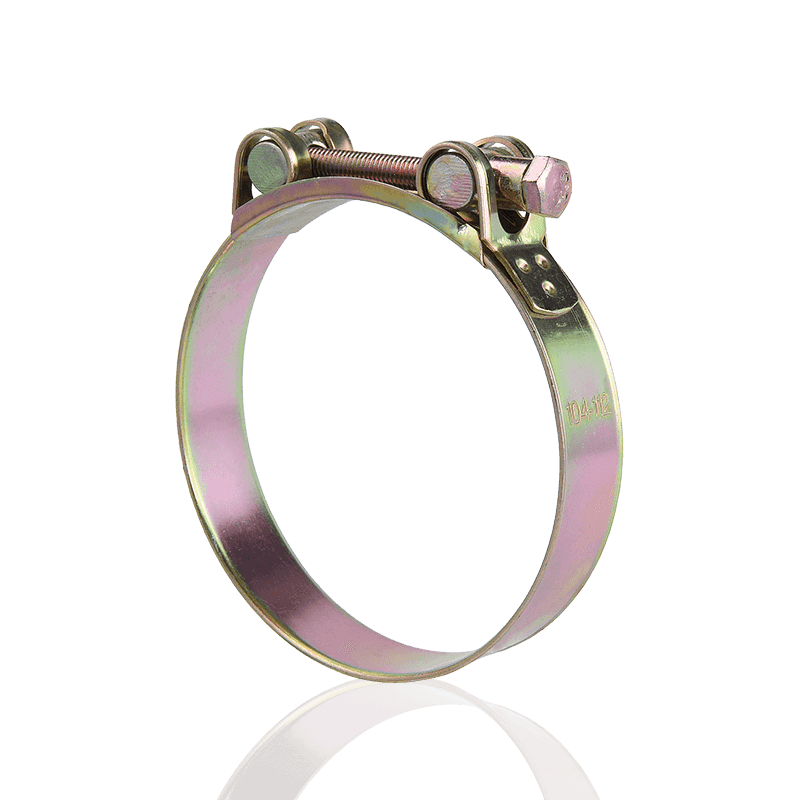
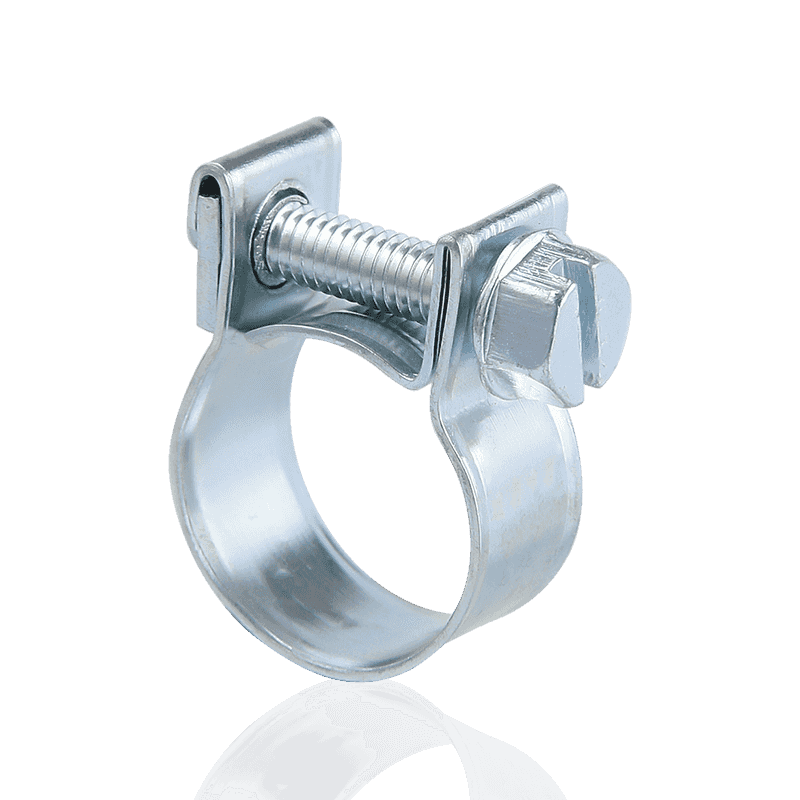
3. Single/Double Ear Clamps
These hose clamps are either "disposable" or "permanent" fasteners, installed and locked using specialized tools.
Features and Principle: They are typically a metal ring with one or two protruding "ears." During installation, the ears are flattened or tightened using specialized pliers, reducing the clamp's diameter and permanently locking it onto the hose. The double-ear design provides stronger securing force.
Advantages: Due to the absence of threads or gaps, they offer a very clean, unobtrusive appearance and provide a highly tamper-proof and leak-proof seal when correctly installed.
Application Scenarios: Commonly used in fuel lines, hydraulic systems, compressed air lines, and other applications requiring high reliability and leak-proof sealing, as well as pipe connections requiring installation in confined spaces.
How to Choose the Right Hose Clamps?
Choosing the right hose clamps requires considering several factors to ensure safe and efficient pipe connections:
- Consider Application Pressure and Vibration: High-pressure or high-vibration environments may require double-ear clamps or heavy-duty threaded clamps.
- Consider Temperature Changes: In situations with drastic temperature changes, spring clamps (constant force clamps) are the best choice to prevent leaks caused by thermal expansion and contraction.
- Consider Installation Space and Tools: Threaded clamps are the easiest to install, requiring only a screwdriver; while disposable clamps (such as single/double-ear clamps) require specialized pliers for installation.
- Consider Material Requirements: In corrosive environments (such as chemical, water treatment, or high-humidity environments), stainless steel clamps made of high-quality materials such as 304 or 316 should be selected to ensure durability and service life.
Whether it's a general-purpose threaded hose clamp, a spring clamp with constant stress function, or a single/double-ear clamp providing a permanent seal, they all play a vital role in fluid management and fastening. A proper understanding of these three main clamp types is fundamental to ensuring reliable, safe, and efficient piping connections. To explore various options, visit our hose clamp section.